Amyloidosis is often misdiagnosed due to its varied symptoms. Don't let this rare disease go undetected; understanding its signs and the importance of an early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and improving your life expectancy.
What are the main causes of Amyloidosis?
- The main cause of amyloidosis is the buildup of an abnormal protein called amyloid, which misfolds and deposits in tissues and organs, disrupting their function.
- In AL amyloidosis, the most common type, abnormal plasma cells in the bone marrow produce misfolded light chain proteins that form these amyloid deposits.
- Transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) is caused by the misfolding of the transthyretin protein, which can be either hereditary or related to the aging process.
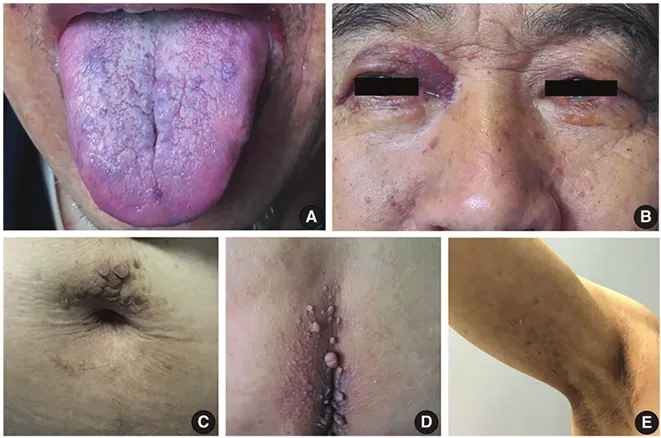
Key symptoms of Amyloidosis to watch for
- Common amyloidosis symptoms are often non-specific and can include severe fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and significant swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet.
- When it affects the heart (cardiac amyloidosis), symptoms may include shortness of breath with mild activity, an irregular heartbeat, and chest pain or pressure.
- Other signs depend on the affected organs and can include numbness in the hands or feet, easy bruising, or signs of kidney distress.
How can you prevent Amyloidosis effectively?
- The underlying amyloidosis causes are not preventable, so the focus of management is on achieving an early diagnosis to slow the progression of the disease.
- The goal of amyloidosis treatment is to stop the production of the abnormal proteins using therapies like chemotherapy, targeted drugs, or specific protein stabilizers.
- Managing symptoms and supporting organ function through diet, fluid management, and other medications is crucial for improving quality of life and overall prognosis.
>>> See more: Gaucher disease – symptoms, causes and treatment
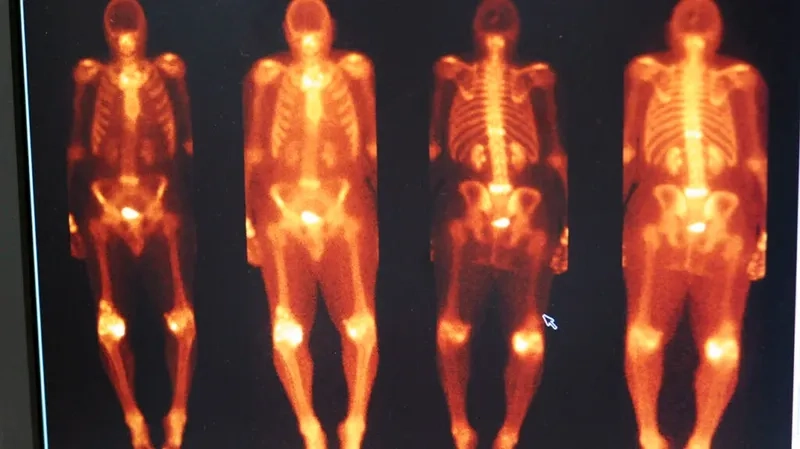
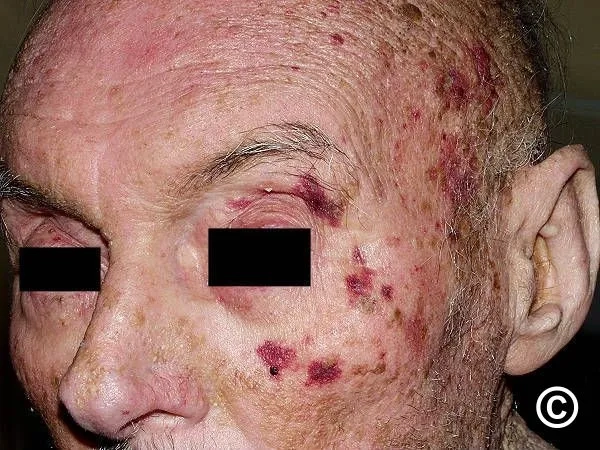
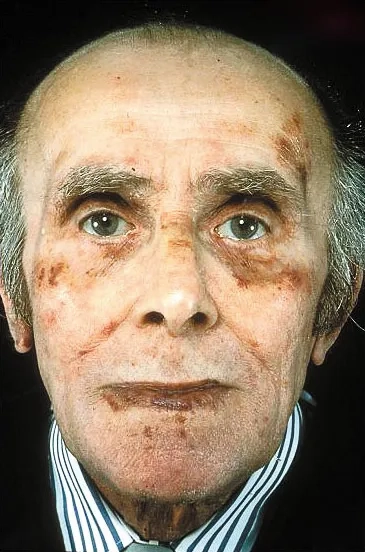
Image of Amyloidosis Amyloid Protein Deposits in Tissue
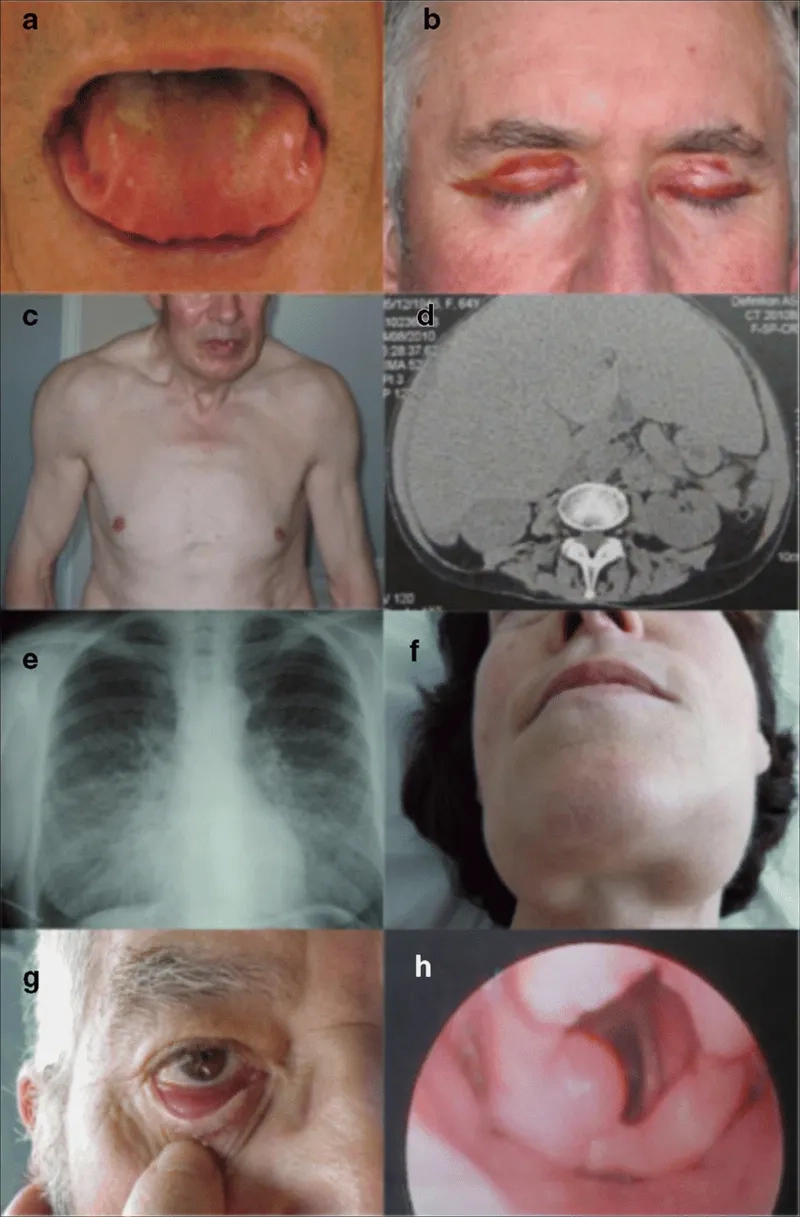
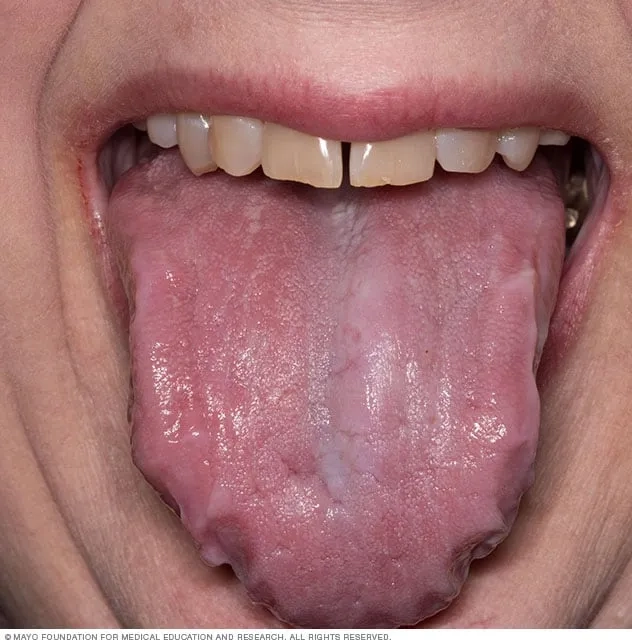
>>> Learn now: Fabry disease – signs, symptoms and care options
Early amyloidosis diagnosis is critical for a better outcome, as life expectancy depends heavily on the type and organ involvement. If you have concerning symptoms, consult a specialist for a comprehensive evaluation and to discuss advanced treatment options.
>>> Don't miss: Pompe disease – symptoms, diagnosis and treatment




