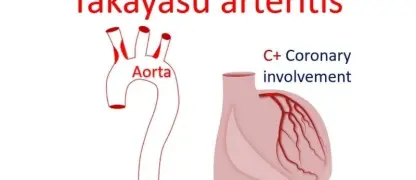
Polyarteritis Nodosa is a rare but serious condition affecting blood vessels. Early recognition of Polyarteritis Nodosa symptoms ensures timely treatment.
What are the main causes of polyarteritis nodosa?
- Immune system dysfunction can cause inflammation of medium-sized arteries, damaging tissues and organs over time.
- Chronic infections, particularly hepatitis B, are strongly associated with triggering polyarteritis nodosa in some patients.
- Genetic predisposition and environmental triggers may interact to increase the risk of developing this condition.
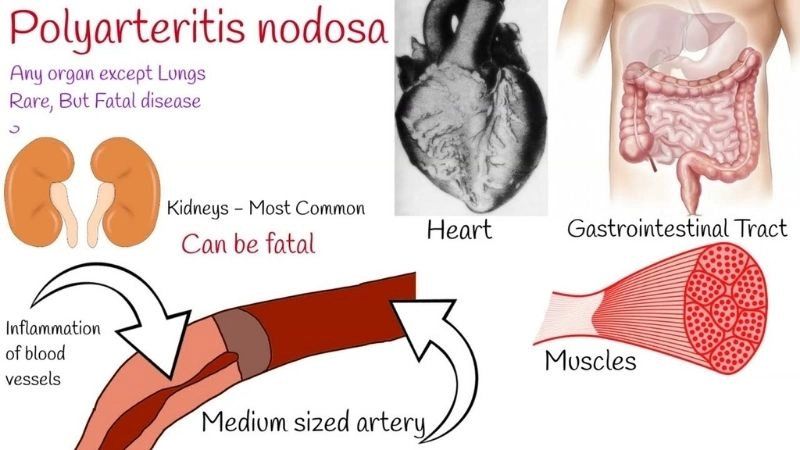
Polyarteritis Nodosa symptoms affecting multiple organs
>>> See more: Raynaud's Phenomenon causes symptoms and treatment guide
Key symptoms of polyarteritis nodosa to watch for
- Persistent muscle and joint pain, often accompanied by fatigue and general weakness, can signal early disease activity.
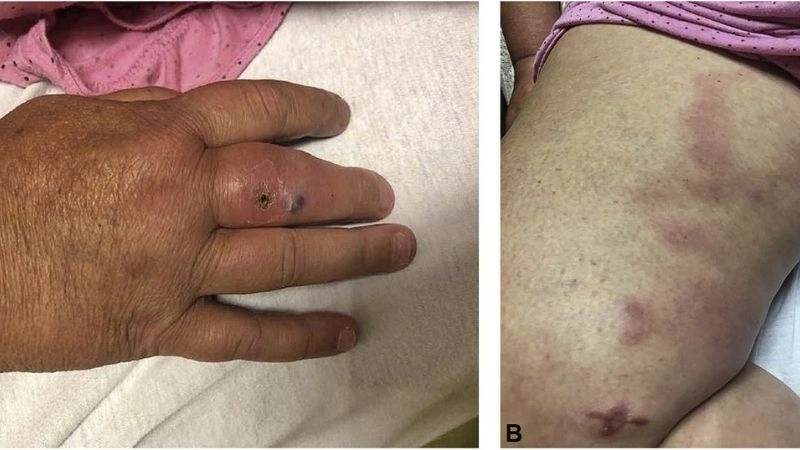
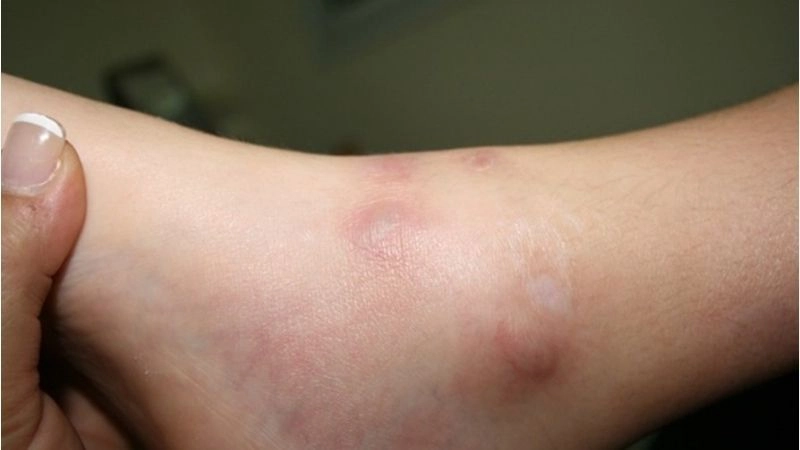
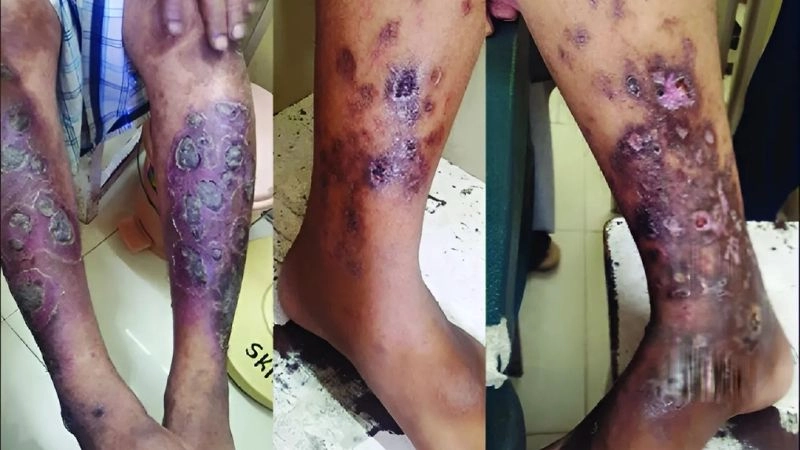
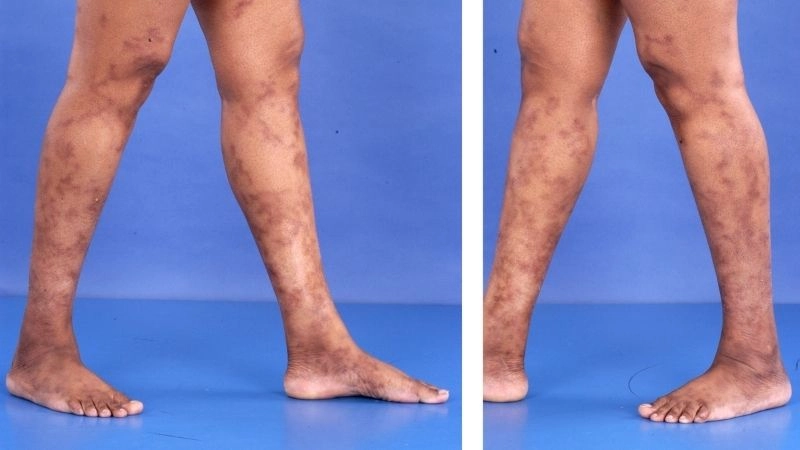
- Skin changes, such as rashes, ulcers, or nodules, often appear due to reduced blood supply to tissues.
- Neurological issues, including numbness, tingling, or peripheral neuropathy, can result from nerve damage.
How can you prevent polyarteritis nodosa effectively?
- Preventing hepatitis B infection through vaccination significantly reduces the risk of developing polyarteritis nodosa.
- Maintaining overall immune health with proper nutrition, exercise, and stress management helps lower susceptibility.
- Regular medical check-ups enable early detection of potential vascular or immune abnormalities.

Polyarteritis Nodosa treatment with medical therapy
>>> See more: Takayasu's Arteritis signs causes and prevention methods
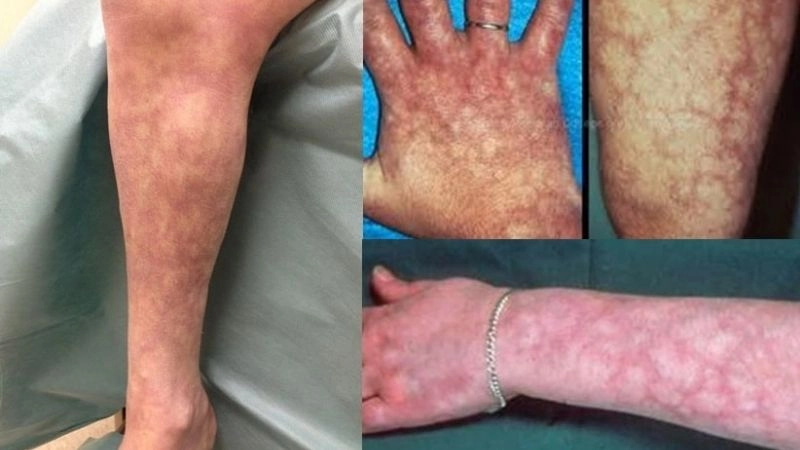
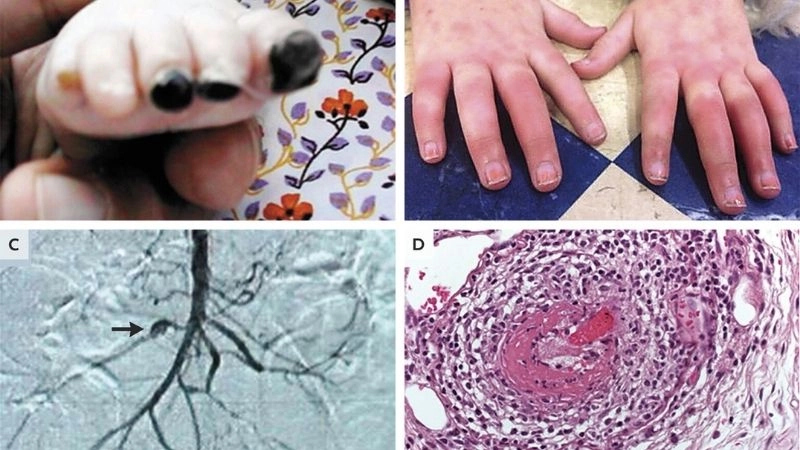
Images visual examples of polyarteritis nodosa
Polyarteritis nodosa is a rare inflammatory disease affecting medium-sized arteries, leading to organ damage. Visual examples often show skin lesions, nodules, or ulcers caused by reduced blood flow.



>>> See more: Giant Cell Arteritis causes symptoms and treatments
Managing Polyarteritis Nodosa requires awareness of its symptoms, causes, and treatments. Stay informed to reduce risks and improve long-term health.