While uncommon, a Human T-lymphotropic Virus infection can lead to serious long-term health issues. Understanding how this virus spreads and recognizing its potential signs is your first line of defense. Don't remain unaware of the risks.
What are the main causes of Human T-lymphotropic Virus Infection?
- The virus primarily spreads from an infected mother to her child, either during birth or, more commonly, through breastfeeding over an extended period.
- It is also transmitted through contaminated blood, such as via unscreened blood transfusions or by sharing needles and syringes among intravenous drug users.
- Sexual contact is another significant mode of transmission, with the virus passing through infected bodily fluids during unprotected sexual intercourse with a carrier.

Key symptoms of Human T-lymphotropic Virus Infection to watch for
- The vast majority of individuals with the infection remain asymptomatic for their entire lives and never develop any related illness, often unaware they have it.
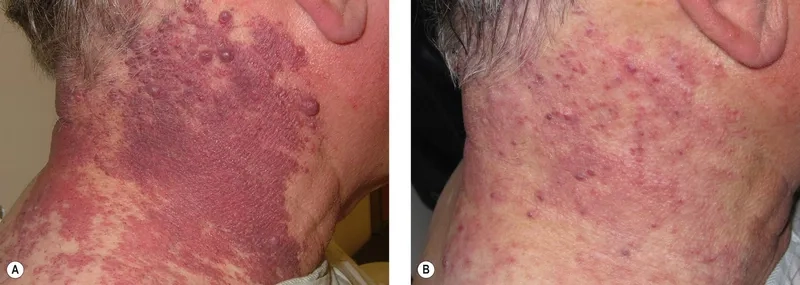
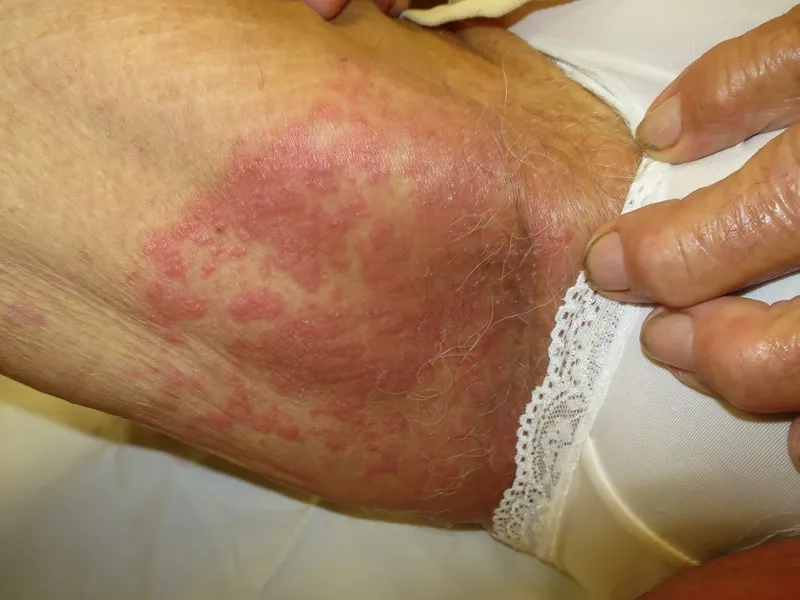
- In a small percentage of cases, it can cause an aggressive cancer called Adult T-cell Leukemia/Lymphoma (ATL), with fatigue and swollen lymph nodes as symptoms.
- It can also lead to a rare progressive nervous system disorder known as HTLV-1-associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP), causing muscle weakness and stiffness in the legs.
How can you prevent Human T-lymphotropic Virus Infection effectively?
- Infected mothers can prevent transmission to their infants by avoiding breastfeeding, which is a key recommendation where safe feeding alternatives are accessible.
- Always ensure that any received blood products are properly screened for HTLV and never share needles to prevent direct blood-borne transmission of the virus.
- Practicing safe sex by consistently and correctly using condoms significantly reduces the risk of acquiring the infection from a partner through sexual contact.
>>> See details: Tuberculosis Signs: Don't Ignore This Persistent Cough
Image of the disease Human T-lymphotropic Virus Infection



>>> See more: Understanding Bartonellosis: Symptoms and Treatment
Awareness is critical for managing the risks associated with HTLV. If you believe you are at risk due to your background or activities, speak with a healthcare provider about your concerns and the possibility of testing.
>>> Details at: Ehrlichiosis: A Guide to this Tick-Borne Illness