Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (PAPVR) is a rare heart condition. Learn symptoms, causes, diagnosis methods, and treatment options effectively.
What are the main causes of partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (PAPVR)?
- A congenital defect where some pulmonary veins connect incorrectly to the right atrium instead of the left atrium, disrupting normal oxygen-rich blood flow.
- Genetic mutations affecting heart development during fetal growth, altering the structure of pulmonary venous connections in the cardiovascular system.
- Associated conditions like atrial septal defect often accompany PAPVR, compounding circulatory abnormalities and worsening cardiovascular stress.
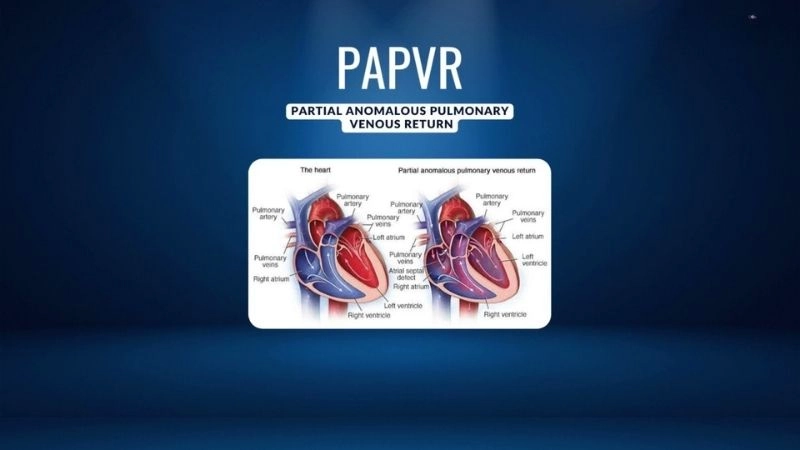
Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return diagnosis explained
>>> See more: How doctors Diagnose Ebstein's Anomaly early and clearly
Key symptoms of partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (PAPVR) to watch for
- Shortness of breath during exertion, caused by inefficient oxygen delivery due to abnormal pulmonary venous connections and reduced cardiac output.
- Frequent respiratory infections in children or adults, as abnormal blood flow increases lung pressure and makes the pulmonary system more vulnerable.
- Fatigue and exercise intolerance, reflecting the heart’s increased workload when handling misdirected pulmonary circulation.
How can you prevent partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (PAPVR) effectively?
- Prenatal care with advanced imaging can detect congenital heart anomalies early, allowing timely planning for medical or surgical intervention after birth.
- Genetic counseling provides guidance for families with a history of congenital heart defects, helping assess risks and make informed reproductive decisions.
- Regular cardiac screenings in at-risk individuals ensure early detection of circulatory abnormalities and reduce the risk of complications.
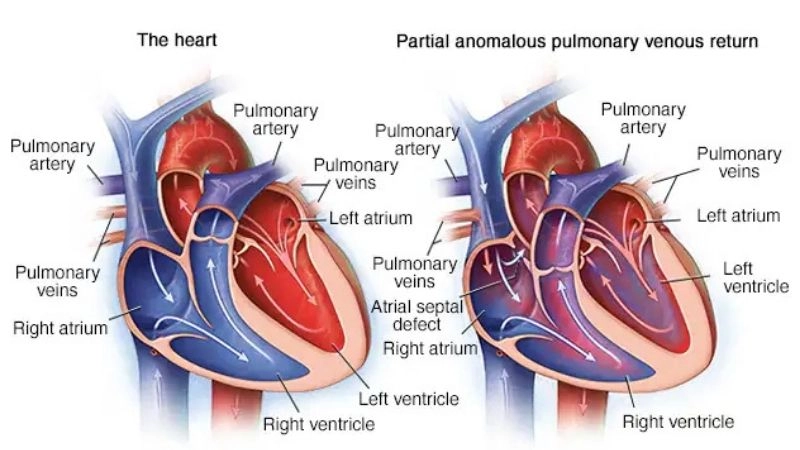
Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return symptoms overview
>>> See more: Early diagnosis of Truncus Arteriosus saves your life
Images visual examples of partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (PAPVR)
Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (PAPVR) is a rare congenital heart defect in which one or more pulmonary veins drain into the right atrium instead of the left atrium.
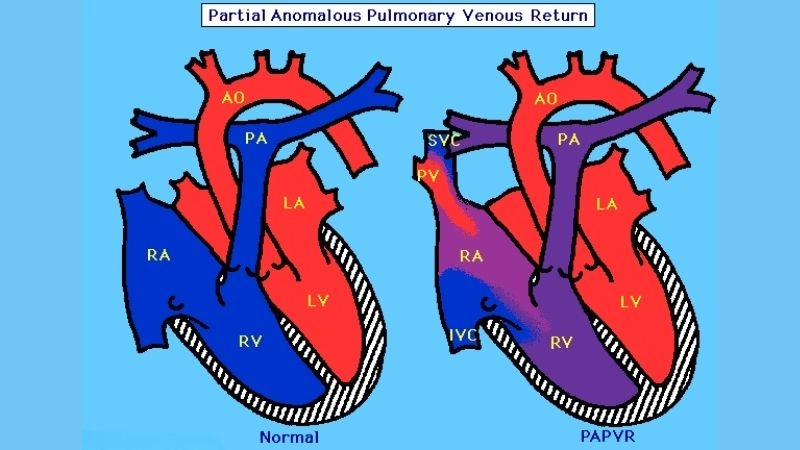
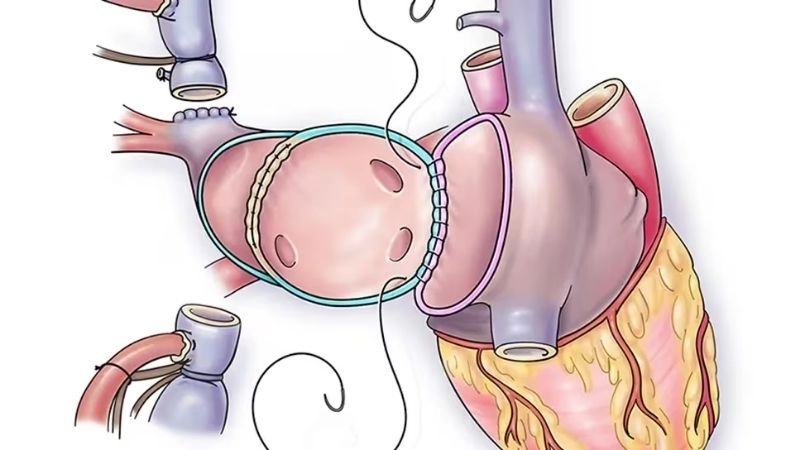
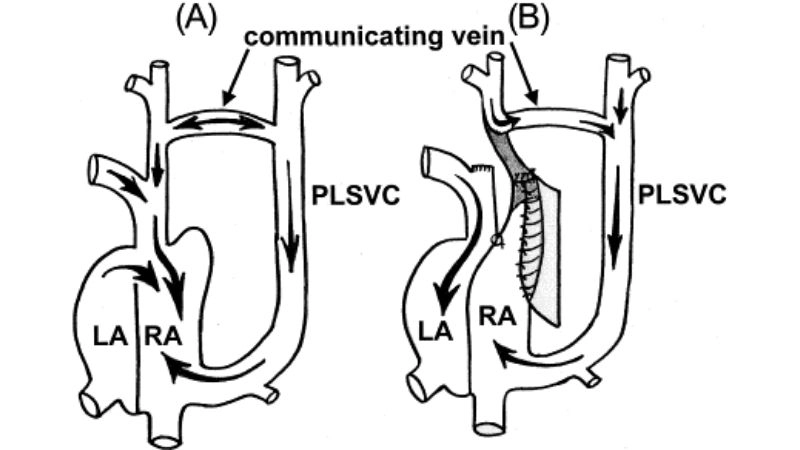
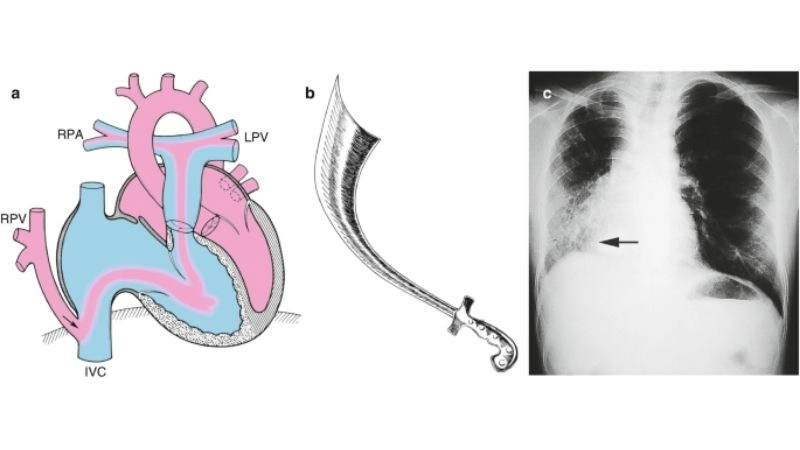
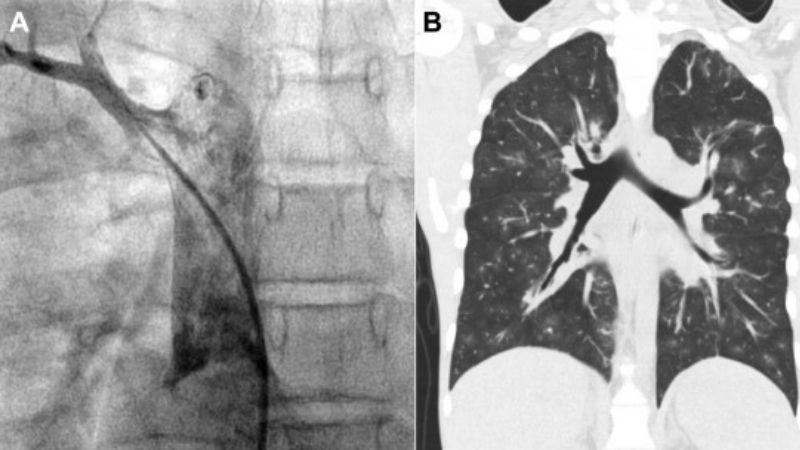
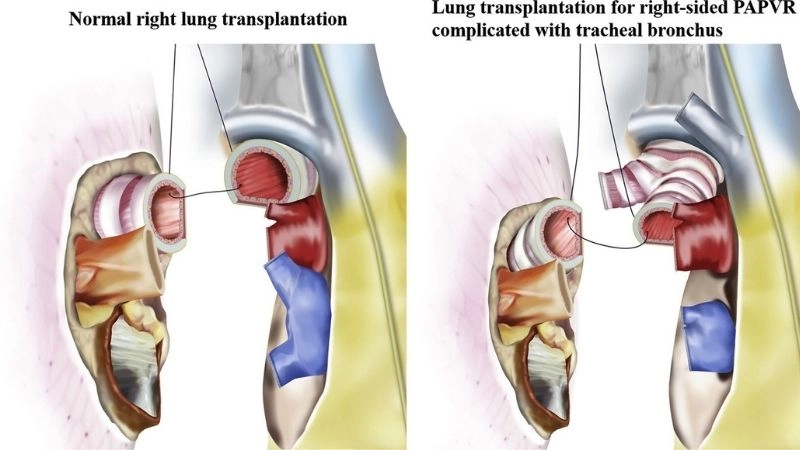
>>> See more: Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR) overview
Understanding Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (PAPVR) helps in early diagnosis, treatment planning, and improving long-term health outcomes for patients.