West Nile Fever is a mosquito-borne viral infection that can cause fever, headache, and body aches. Understanding its symptoms and prevention is key to staying safe.
What are the main causes of West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Fever is primarily caused by infection through bites from infected mosquitoes, which carry the virus from birds to humans.
- Blood transfusions or organ transplants from infected donors can rarely transmit West Nile Fever to recipients.
- Individuals with weakened immune systems or older adults are more susceptible to severe infection and complications.
Key symptoms of West Nile Fever to watch for
- Early symptoms include fever, headache, body aches, and fatigue, often resembling a mild flu-like illness.
- Some patients may develop a skin rash, swollen lymph nodes, or eye pain as the infection progresses.
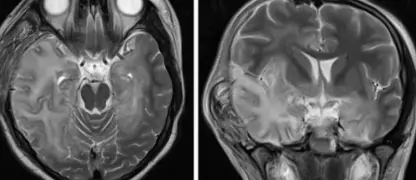
- Severe cases can lead to neurological issues such as confusion, seizures, muscle weakness, or paralysis.

>>>Explore now: St. Louis Encephalitis key facts you should understand
How can you prevent West Nile Fever effectively?
- Use insect repellent containing DEET and wear protective clothing to reduce mosquito bites, especially during peak mosquito activity.
- Eliminate standing water around homes, such as in flowerpots or gutters, to minimize mosquito breeding sites.
- Ensure window and door screens are intact and consider using mosquito nets in high-risk areas to prevent exposure.
>>>Explore now: Everything you should know about japanese encephalitis
Image description of West Nile Fever
West Nile Fever is a mosquito-borne viral infection that affects humans and animals, sometimes leading to severe neurological symptoms in rare cases.








>>>Explore now: Viral encephalitis explained key facts you must know
By recognizing the signs of West Nile Fever and following proper prevention methods, you can protect yourself and your family from infection and reduce the risk of severe complications.